| |
|
|
| |
Overview
of SCADA SYSTEMS |
|
| |
|
|
| |
SCADA
Terminology |
|
| |
SCADA
is an acronym for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition.
Data
Acquisition : Gathers information from widely distributed processes
Supervisory
Control : Calculate and give limited control instructions to distant
process facilities
Historical
Background
1960s:
Radio
Telemetry : weather monitoring using unmanned balloon/rocket.
Hardwired
Remote Monitoring : oil & gas and processing industries
1970s:
Two-way
radio telemetry.
Mini-computer.
Distributed
Process Control System (DCS).
Programmable
Logic Controller (PLC).
1980s:
Low
cost microcomputer (PC).
Satellite
Communications.
Cellular
Telephone.
1990s:
Local
Area Network (LAN).
High
Speed Communication Devices.
Internet.
| |
| |
Goals
to Achieve |
|
| |
Technical :
Safety.
Increased productivity.
Equipment protection and maintenance.
Operational optimization.
Energy saving.
Immediate access to inventories, receipts, deliveries, etc.
|
|
| |
Economical :
Plant-wide optimization.
Optimization of personnel utilization.
|
|
| |
Applicable
Processes |
|
| |
Widely distributed processes; spreading over large areas
Require frequent, regular, or immediate intervention
High cost of routine visits to monitor facility operation
Examples :
Oil and gas production facilities,
Pipelines for gas, oil, chemical, or water,
Electric power transmission system
Railroad traffic
Feed water purification plant
Building automation
|
|
| |
Data
Communications |
|
| |
One MTU can exchange data with one or more RTUs
Data exchange within MTU and RTUs follows a pre-defined set of rules
called communication protocol
Data is encoded as binary signal (series of ones and zeros)
This binary signal is modulated before it propagates through communication
medium
Two-way communications (half or full duplex)
serial transmission (asynchronous/synchronous)
Leased or non-leased line
Guided or wireless medium :
radio link (UHF, VHF, microwave, satellite)
cable link (telephone, twisted pair, coaxial, power line carrier)
fiber optic
Railroad traffic
Etc.
|
|
| |
Remote
Terminal Unit (RTU) |
|
| |
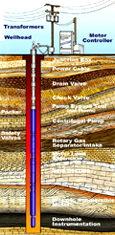
Placed at remote plant location
Integrated with instrumentation and control systems (PLC or DCS)
Functions :
Gathers information from the field
Send the information to MTU
Process the supervisory control instruction from MTU
|
|
| |
Device
Network |
|
| |
Actuator/Sensor Level :
Analog signals of the conventional sensors and actuators are transmitted
via two-wire cable.
One dedicated two-wire cable is required for each sensor/actuator,
Analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters are required
to enable interfacing and communications with other intelligent
devices (programmable controllers, smart transmitter, fieldbus devices).
|
|
| |
Plant
Network |
|
| |
RTU to Sub-MTU to MTU connection
Medium :
guided : cable, telephone, ISDN, optical fiber, etc.
wireless : broadcast radio, microwave, satellite
|
|
| |
Protocol :
DH, DH+, DH-485, ControlNet.
Modbus, ModbusPlus, ModbusTCP
Hostlink
DNP.
|
|
| |
Corporate/Enterprise
Network |
|
| |
Ethernet
TCP/IP
Corporate Applications :
Real time asset management
Business support
Marketing & sales
Procurement
Manufacturing
Distribution
Data warehouse
|
|
| |
Master
Terminal Unit (MTU) |
|
| |
Customized configuration for each applications
Connected to Local Area Network (LAN)
Equipped with auxiliary devices (data storage, console, pointing
devices, etc)
Functions :
Collect process information from RTUs and share the information
on the LAN
Online operator interface (MMI)
Send supervisory control instruction to RTUs
Alarm management
Report generation
System security
Central data processing
|
|
| |
Man
Machine Interface (MMI) |
|
| |
Provides human access to field automation system
Operational
Maintenance & troubleshooting
Development
|
|
| |
Function :
Communicates with field I/O from Programmable Logic Controllers
(PLCs), Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and other devices.
Gives up-to-date plant information to the operator using graphical
user interface.
Translates operator instruction into the machine
Engineering development station
Operator station
|
|
| |
Plant information :
Process Variables.
Device status.
Alarms
Control Loops
Etc
|
|
| |
Presentation Method :
Graphics Trending
Charts
Reports
Animation
Etc.
|
|
| |
Equipment :
Keyboard
Mouse or other pointing devices
Touchscreen or CRT
Etc.
|
|
| |
User
Applications |
|
| |
Development tools is provided by SCADA system supplier (scripting
tools)
Examples :
Meter gross/net computation
Pipeline terminal display
Pipeline inventory
Transient modeling systems
Dynamic leak detection
Pipeline simulator
Compressor optimization
Automatic well testing
Well revenue calculation
etc.
|
|
| |
System
Database |
|
| |
Store historical process information for engineering, production,
maintenance, and business purposes.
Features :
Engineering units conversion
Analog value filtering
Value limit checking
|
|
| |
Standardized Data Structure :
Analog point structure
Status point structure
Accumulator point structure
Container points
User defined structure
|
|
| |
Each point in the database has a number of associated parameters,
all of which can be referenced relative to a single tag name. |
|
| |
OLE
for Process Control (OPC) |
|
| |
Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) for Process Control
A standard for process automation (SCADA) communications
A standard software mechanism for sharing data between process automation
(SCADA) of different manufacturers
OPC is based on Microsoft OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) and
DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model)
FOPC advantage :
Simple to implement
Flexible to accommodate multiple vendor needs
Provide a high level of functionality
Allow for efficient operation
|
|
| |
Plant-Office
Data Integration |
|
| |
Networking has been successfully implemented from field device level
up to management level.
Data can easily be interchanged between applications in the same computer
or different computers over a network.
SCADA system can give an immediate response needed from field device
to management system.
Real-time plant information can be transferred to office application.
Corporate information system must be designed to meet its business
process. |
|
| |
Dynamic
Data Exchange (DDE) |
|
| |
An application protocol that allows data exchange on real-time basis
on Windows/WindowsNT platforms.
NetDDE = Dynamic Data Exchange over network.
|
|
| |
Web-based
Process Monitoring |
|
| |
Internet browser as an acceptable MMI standard will minimizes operator/user
training by providing a familiar operating environment
Many visualization techniques are available (JavaScript, Java, Shockwave/Flash,
etc)
Extra development effort is not needed since SCADA supplier software
usually provide integrated web-based and application specific MMI
development
Allows the users (e.g. : supervisor/manager) to monitors process operation,
documents and reports either in the Intranet or Internet.
Secured network design is a must to avoid cyber risk such as hacking
attempts and virus. |
|
| |
Summary |
|
| |
SCADA is a two-way system : remote monitoring & controlling.
Applicable to widely distributed processes.
Two way communication system is required.
Basic Elements of SCADA :
Master Terminal Unit (MTU)
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)
Communications Equipment.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|